 |
| Types of Databases |
Thus, database is defined as a set of data that has a regular structure and that is organized in such a way that a computer can easily find the desired information.
Databases offer an organized mechanism for storing, managing and retrieving information.
Types of Databases
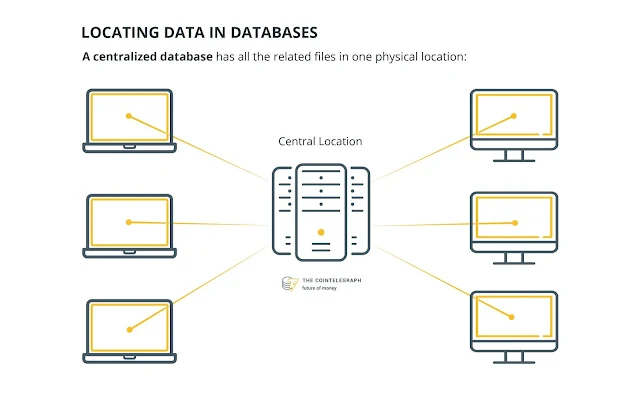
1. Centralized Database
-
Users from different location can access and
process data using application procedures
-
For verification and validation of end users,
different authentication procedures are applied, which is handled by local area
office
-
Example:
“Nepal Telecom (NTC) has a centralized
database for registration of applications for new telephone connections. The
data regarding the applicant are received from a local area office of NTC.
Data validation and verification
is carried out by the application programs at the central computer center, and
a registration number is allotted by the application programs located at the
central facility. The local area office keeps on recording it and hardly does
any processing”
2. Distributed Database
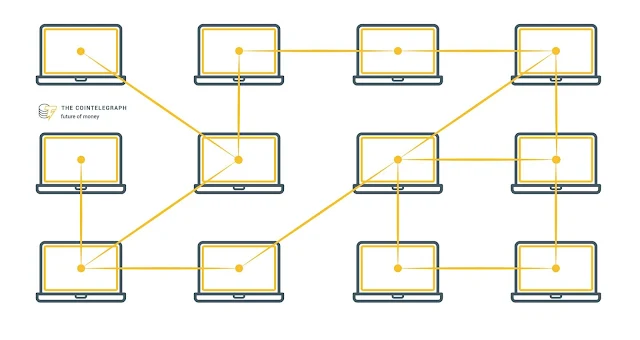 |
| Distributed Database |
-
Distributed Database has contributions from the
common database as well as the information captured by local computer.
-
All databases are connected to each other with
the help of communication links which helps them to access the distributed data
easily.
- For Example: “imagine a distributed database as a one in which various
portions of a database are stored in multiple different locations(physical)
along with the application procedures which are replicated and distributed
among various points in a network.”
-
There are Two kinds of Distributed Databases
(DDB). They are
-
a.
Homogeneous DDB: The databases which have same underlying hardware and run
over same operating systems and application procedures are known as homogeneous
DDB, for e.g. All physical locations in a DDB.
-
b. Heterogeneous DDB: Whereas, the operating systems,
underlying hardware as well as application procedures can be different at
various sites of a DDB which is known as heterogeneous DDB.
3. Personal Database
-
Data Collected and Stored on a Personal
Computers
-
Small and Easily manageable
-
Data is generally used by the same department of
an organization
-
Accessed by small group of people
-
These DBs are generally subject specific and
user designed
-
They use simple and less powerful DBMS packages
available on PCs and may not have all the features of Relational Database
Management System (RDBMS) but have
similar limited features.
4. End-user Database
-
Here, End User is not concerned about the
transaction or operations done at various levels and is only aware of the
product which may be a software or an application.
-
This is a shared database which is specifically
designed for the end user like managers at different levels.
-
These managers may not be concerned about the
individual transactions as in operational databases. Rather, they would be more
interested in summary information.
-
Although, the operational databases can also
generate summary information from the transaction details, they would be quite
slow as they are not designed for this purpose.
5. Commercial Database
-
These are the paid versions of huge databases
designed uniquely for the users who want to access information for help.
-
These databases are subject specific, and one
cannot afford to maintain such a huge information
-
Such database is provided through commercial
links
-
These databases may offer statistics regarding
commodity, foreign exchange and stock markets, companies and their performance,
importers and their buying patterns, decided case laws, etc.
6. NoSQL Database
-
NoSQL is an acronym for “Not Only SQL”
-
It is an alternative to traditional RDBMS and
are especially useful for working with large sets of distributed data.
-
NoSQL databases can be schema agnostic, allowing
unstructured and semi-structured data to be stored and manipulated (Rouse,
2011).
Different types of NoSQL databases
are as follows
a.
Document
databases: These databases pair each key with a complex data structures
known as a document. Documents can contain many different key-value pairs, or
key-array pairs, or even nested documents.
b.
Graph
Stores: These databases are used to store information about networks of
data, such as social connections. Graph Stores include Neo4J and Giraph.
c.
Key-Value
Stores: These are the simplest NoSQL databases. Every single item in the
database is stored as an attribute name (or ‘key’), together with its value.
Example of key-value stores are Riak and Berkeley DB. Some key-value stores,
such as Redis allow each value to have a type, such as ‘integer’, which adds
functionality.
d.
Wide-Column
Stores: Databases such as Cassandra and HBase are optimized for queries
over large datasets, and store columns of data together, instead of rows (MongoDB, 2019).
7. Operational Database
-
Data related to the operations of enterprise are
stored
-
This database Manages and Stores data in real
time.
-
Generally, such databases are organized on
functional lines such as marketing, production, employees, etc.
-
Operational database is the source for a data
warehouse.
-
Elements in an Operational database can be added
and removed on the fly.
-
These databases can be either SQL or NoSQL
based, where the latter is geared toward real-time operation.
-
These data are collected from sensors, machines,
IOT, Media, Transactions, etc.
8. Relational Database
-
These databases use table-like schemas and store
the data in disk
-
They are good to store business data
- Here, database is categorized by a set of tables
and the tables consists of rows and columns where the columns has an entry for
data for a specific category and rows contains instance for that defined
according to the category.
-
The Structured Query Language (SQL) is the
standard user and application program interface for a relational database.
-
Some of the major RDBMS are SQL Server, Oracle,
MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.
9. Cloud Database
-
Database that is accessible to client from the
cloud and delivered to users on demand via the internet from a provider’s
server (Webopedia.com, 2019).
-
A type of database service that is built,
deployed and delivered through a cloud platform.
-
Also referred to as Database-as-a-Service
(DBaaS), cloud databases can use cloud computing to achieve optimized scaling,
high availability, multi-tenancy and effective resource allocation.
-
A cloud database typically works as a standard
database solution that is generally implemented through the installation of
database software on top of a computing/infrastructure cloud (Techopedia.com,
2019).
-
It may be directly accessed through web browser
or a vendor provided API for application and service integration.
10. Object-oriented Database
-
Object-oriented Database (OODB) represents data
in the form of objects and classes
-
These databases follow the fundamental
principles of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
-
Object – Oriented Programming + Relational
Database = Object – Oriented Database Model (Sivabalan, 2019)
-
An object-oriented database is organized around
objects rather than actions, and data rather than logic. For example: a
multimedia record in relational database can be a definable data object, as
opposed to an alphanumeric value.
11. Graph Database
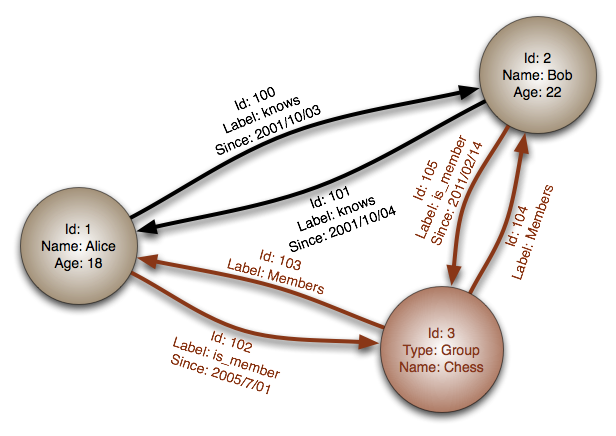 |
| Graph Database Property Graph |
- Also called a graph-oriented database, is a type of NoSQL database that uses graph theory to store, map and query relationships.
-
It is essentially a collection of nodes and
edges. Each node represents an entity (such as a person or business) and each
edge represents a connection or relationship between two nodes. Every node in a
graph is defined by a unique identifier, a set of outgoing edges and/or
incoming edges and a set of properties expressed as key/value pairs.
-
Graph Database are well-suited for analyzing
interconnections, which is why there has been a lot of interest in using graph
databases to mine data from social media.
-
They are also useful for working with data in
business disciplines that involve complex relationships and dynamic schema,
such as supply chain management, identifying the source of an IP telephony
issue and creating “customers who bought this also looked at…” recommendations
(Rouse, 2019).
References
Algorri, M.
(2016). [online] Available at:
https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-different-types-of-databases [Accessed 18
Mar. 2019].
MongoDB.
(2019). NoSQL Databases Explained. [online] Available at:
https://www.mongodb.com/nosql-explained [Accessed 18 Mar. 2019].
Rouse, M.
(2011). What is NoSQL (Not Only SQL database)? - Definition from
WhatIs.com. [online] SearchDataManagement. Available at:
https://searchdatamanagement.techtarget.com/definition/NoSQL-Not-Only-SQL
[Accessed 18 Mar. 2019].
Rouse, M.
(2019). What is graph database? - Definition from WhatIs.com.
[online] WhatIs.com. Available at:
https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/graph-database [Accessed 18 Mar.
2019].
S, S.
(2018). Database: Six Important Types of Databases | Business Management.
[online] Your Article Library. Available at:
http://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/database/database-six-important-types-of-databases-business-management/10375
[Accessed 18 Mar. 2019].
Sam, S.
(2018). Types of databases. [online] Tutorialspoint.com. Available
at: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/Types-of-databases [Accessed 18 Mar. 2019].
Sivabalan, V.
(2019). What is an Object-Oriented Database? | Study.com. [online]
Study.com. Available at:
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-an-object-oriented-database.html
[Accessed 18 Mar. 2019].
Techopedia.com.
(2019). What is a Cloud Database? - Definition from Techopedia.
[online] Available at:
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/26523/cloud-database [Accessed 18 Mar.
2019].
Webopedia.com.
(2019). What is a cloud database? Webopedia Definition. [online]
Available at: https://www.webopedia.com/TERM/C/cloud_database.html [Accessed 18
Mar. 2019].









![Advertisement [ad]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEgVAiCox6-vLXsNZas8ks-nfos0PgdnL4yClmlqOkl92t7zGdYYiLBy9AHMZFxBYe06DVmN6JGQ9S0P3iClXk8l43FIQPDyAcx_uMmV0bN9JlKjTzOAi7YjmQo6cuvHgkEO76L-hcqV-TWE29v93eeFby8MOAOuJ8DcilHTPpfP8aKg8TG9uYCDaMxcr8H1=s600)


Comments